Massachusetts Tenant-Landlord Rental Laws & Rights for 2024
Overview of Massachusetts Tenant-Landlord Laws
Understanding tenant-landlord laws in Massachusetts is crucial for ensuring a fair and balanced rental relationship. These laws are designed to protect both parties, outlining their rights and responsibilities in various aspects of the rental process.
Key areas covered by Massachusetts law include rental agreements and leases, security deposits, rent payments and increases, habitability and repairs, access to rental property, termination of tenancy, tenant privacy and fair housing, landlord rights and access, eviction defenses, and dispute resolution.
Rental agreements and leases in Massachusetts must specify essential terms and conditions, and both landlords and tenants must adhere to their obligations. Security deposits are regulated to prevent unfair practices, with clear guidelines on handling and returning deposits. Rent payments are due as specified in the lease, with reasonable late fees permitted, and proper notice is required for rent increases.
Landlords have a duty to maintain habitable premises, while tenants must keep the property clean and report necessary repairs. Landlords must also provide advance notice before entering a rental unit, except in emergencies. Eviction processes must follow strict legal procedures, and tenants have several defenses and protections against wrongful eviction.
Both landlords and tenants in Massachusetts have resources available to help them understand and navigate these laws, ensuring a cooperative and legally compliant rental experience.
Rental Agreements and Leases
In Massachusetts, rental agreements and leases are legally binding contracts that outline the rights and responsibilities of both landlords and tenants. Key aspects typically covered include the rental amount, payment due dates, length of tenancy, security deposit details, rules regarding guests or subletting, and any other negotiated terms.
Both landlords and tenants have certain obligations under Massachusetts law. Landlords must provide habitable premises by ensuring the rental unit meets minimum standards for safety, sanitation, and essential utilities. They also have a duty to make necessary repairs in a timely manner. Tenants are obligated to pay rent on time, keep the property clean and undamaged beyond normal wear and tear, and follow all rules specified in the lease agreement.
When negotiating a lease, tenants may request certain modifications or additions to better suit their needs. Common areas for negotiation include allowing pets, parking accommodations, amenity access, or even rent control provisions if the rental is not already regulated. However, landlords cannot include any illegal, discriminatory, or unconscionable terms.
Massachusetts requires landlords to include certain disclosures in the rental agreement, such as the property owner's name and address, banking institution where security deposits are held, and any conditions that could render the premises uninhabitable. Allowable terms can cover a wide range of issues like repairs, guests, subletting, and other rules of occupancy. Prohibited terms include waiving the landlord's legal obligations, authorizing unlawful behavior, or infringing on tenants' basic rights.
Once a lease is signed, any modifications require agreement from both parties. If the tenancy becomes month-to-month after the initial term expires, landlords must provide proper notice, often 30 days, before enacting any changes to rent or other terms. Clear communication and documentation are critical for amending a lease to avoid potential disputes down the line.
Security Deposits
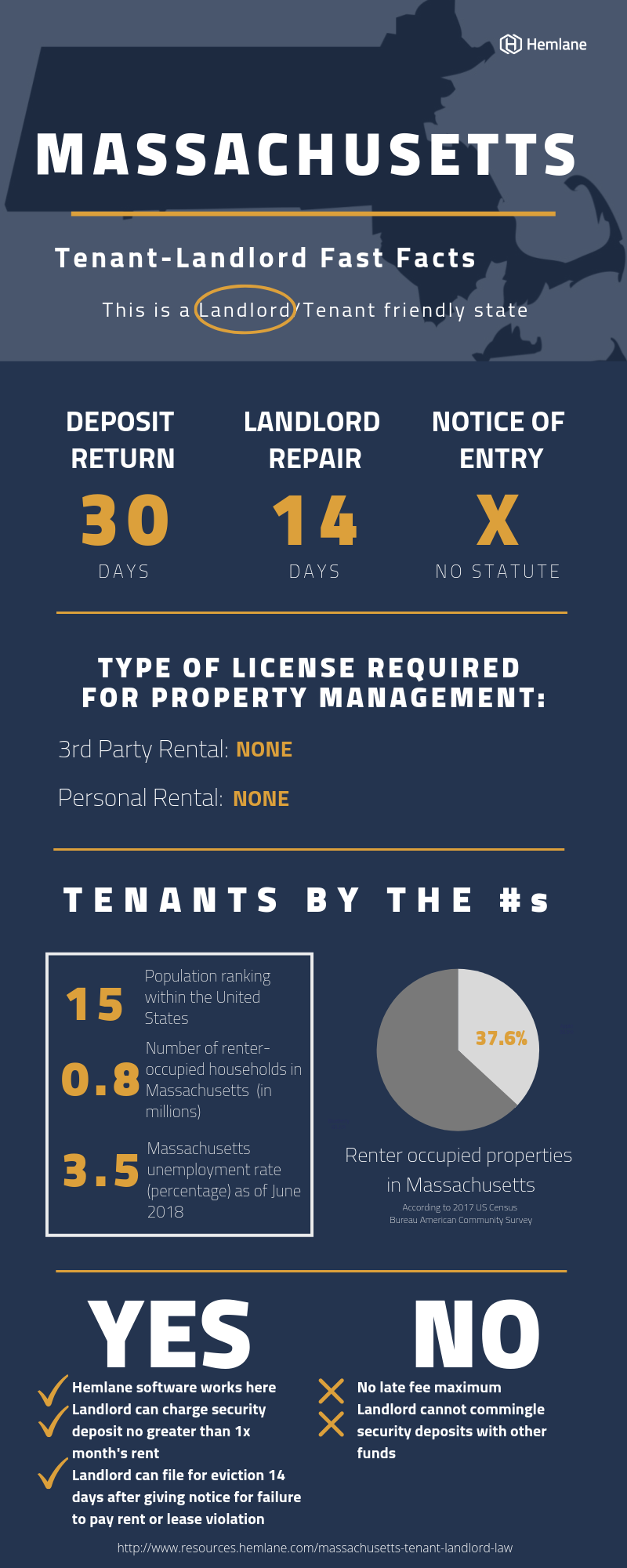
Security deposit laws in Massachusetts regulate the amount a landlord can collect for a security deposit, how the deposit must be handled, and the procedures for returning it at the end of a tenancy.
The maximum security deposit a landlord can require in Massachusetts is equal to first month's rent. For example, if the monthly rent is $1,200, the largest security deposit allowed is $1,200. There are no exceptions that allow a landlord to collect a higher deposit.
Landlords must provide tenants with a written statement of conditions at the start of tenancy, detailing any existing damage to the rental unit. This protects both parties by documenting the condition before the tenant moved in.
Any security deposit collected must be held in a separate interest-bearing account, and landlords are required to pay annual interest at 5% or the actual bank rate, whichever is lower. Landlords must provide tenants with an annual statement showing interest accrued.
When a tenant moves out, the security deposit must be returned within 30 days. If any deductions are taken out for unpaid rent, excessive damage beyond normal wear and tear, or other allowed charges, the landlord must provide a detailed written accounting of deductions with the remaining deposit refund.
Allowable deductions from the security deposit include repairing any excessive damage beyond normal wear and tear, replacing missing items, unpaid rent, and any other expenses caused by tenant negligence or violation of the lease. However, landlords may not deduct for routine repainting or carpet cleaning costs considered normal wear and tear.
If a landlord fails to return the security deposit within 30 days or makes improper deductions, the tenant can sue to recover triple the amount wrongfully withheld, plus interest and court costs. These strict rules aim to protect tenants from unfair withholding of security deposits.
Rent Payments and Rent Control
In Massachusetts, rent is typically due at the beginning of each rental period as specified in the lease agreement. Most leases will set the rent due date as the 1st of the month. Landlords are allowed to charge late fees if rent is paid after the due date, but those fees must be reasonable and specified in the lease. A typical late fee might be a flat rate like $50 or a percentage like 5% of the monthly rent.
Tenants have the right to make partial rent payments, and landlords cannot legally refuse partial payments. If a tenant makes a partial payment, that amount must be accepted and credited to their rent balance. However, landlords can still charge late fees on any remaining unpaid portion.
When it comes to rent increases, Massachusetts requires advance written notice. For month-to-month tenancies, landlords must provide at least 30 days' notice before increasing rent. For leases with a set term (e.g. 1 year), landlords cannot increase rent until the lease term expires. Any rent increase requires proper notice of at least 30 days (or the rental period, whichever is longer).
For existing tenants renewing a lease, landlords cannot raise rent in a discriminatory manner or as retaliation against the tenant. Any rent increase must be reasonably related to operating costs, fair market value, or increased housing services. Excessive or unjustified rent hikes may be considered illegal.
Rent Control Laws
Massachusetts does not have statewide rent control laws. However, some municipalities, like Cambridge and Brookline, have enacted their own rent control ordinances in the past. These local laws typically limit the amount landlords can increase rent annually, often tying increases to a percentage of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) or setting a fixed cap.
It is important for tenants and landlords to check their local regulations to see if any rent control measures are in place in their specific area. These measures aim to protect tenants from excessive rent increases and maintain affordable housing within the community.
Habitability and Repairs
In Massachusetts, landlords have a legal duty to ensure rental units are habitable and to make necessary repairs to keep the premises fit for human occupation. This obligation, known as the implied warranty of habitability, requires landlords to provide premises that are clean, safe, and compliant with all applicable building and sanitary codes.
Landlords must maintain structural elements like walls, floors, and roofs in good repair. They are also responsible for ensuring vital services like heat, water, electricity, and plumbing are operational. Heating facilities must be able to provide minimum temperatures during winter months as specified by state law.
When a landlord fails to provide essential services or make necessary repairs after receiving proper notice from the tenant, the tenant may have grounds for rent withholding, repair-and-deduct remedies, or potentially terminating the rental agreement. However, tenants should follow specific notice requirements and procedures under Massachusetts law.
If a rental unit becomes uninhabitable due to fire, flood, or other catastrophe that is no fault of the tenant, the tenant may be able to vacate the premises and terminate the lease. Landlords cannot demand rent for periods when the unit is uninhabitable through no fault of the tenant. Tenants should promptly notify the landlord of any conditions that render the premises unlivable.
Tenants also have the right to a reasonable accommodation for any health condition that requires modifications to the rental unit. Landlords must allow reasonable modifications at the tenant's expense. Overall, Massachusetts law prioritizes providing safe, decent, and habitable housing for all tenants.
Access to Rental Property
In Massachusetts, landlords have a right to enter a rental unit to inspect the premises, make necessary repairs, or show the unit to prospective tenants or buyers. However, there are specific notice requirements to protect a tenant's right to privacy.
A landlord must provide reasonable advance notice, defined as at least 24 hours, before entering a rental unit so the tenant can prepare accordingly. The notice must state the intended date, approximate time frame for entry, and purpose of the landlord's entry. Landlords cannot abuse this access right for the purpose of harassing or intimidating tenants.
Tenants have a reasonable expectation of privacy in their rental home. Landlords cannot enter without proper notice except in cases of emergency that threaten health or safety. Even with notice, landlords should request a tenant's permission before entering living areas of the rental unit. Tenants are not required to allow entry for the landlord's convenience alone if the request is excessive.
There are limited exceptions for entry without advance notice, such as if a tenant has been legally evacuated or has abandoned the property. However, in general, landlords must respect tenant privacy rights and provide proper notification before entering a rental unit per Massachusetts law.
Termination of Tenancy
In Massachusetts, there are specific notice requirements and grounds for eviction that landlords must follow when terminating a tenancy. For tenants with a lease, the landlord must provide proper written notice as specified in the lease agreement, usually 30-60 days before the lease expires. If there is no lease or the lease has expired, landlords must give tenants at least 30 days' written notice to terminate a month-to-month tenancy.
Allowable grounds for eviction in Massachusetts include nonpayment of rent, substantial violation of the lease terms, causing substantial damage to the premises, or creating a serious nuisance. A landlord cannot evict in retaliation against a tenant for exercising their legal rights.
The eviction process begins with the landlord serving the tenant with a legally proper notice, such as a 14-day Notice to Quit for nonpayment of rent. If the tenant does not move out after the notice period, the landlord must file an eviction complaint with the court and attend a hearing. If the court rules in favor of the landlord, they will issue an execution order allowing the eviction to proceed. Law enforcement can then legally remove the tenant if they refuse to leave by the court's deadline.
Landlords must strictly follow all required procedures and timelines in the eviction process. Tenants have the right to dispute an eviction in court if proper protocols were not followed. Both parties can benefit from understanding their rights and responsibilities under Massachusetts law regarding terminating a tenancy.
Tenant Privacy and Fair Housing
In Massachusetts, landlords are prohibited from discriminating against tenants based on race, color, national origin, religion, sex, familial status, disability, sexual orientation, gender identity, age, marital status, ancestry, military status, or source of income. This covers all aspects of the rental process, including advertising, screening applicants, setting terms and conditions, and terminating a tenancy.
Tenants have a right to reasonable privacy and landlords must provide proper notice (usually 24 hours except in emergencies) before entering a rental unit. Landlords cannot unreasonably restrict guests from entering the premises. However, they may limit the amount of time guests can stay to prevent unauthorized occupants.
Massachusetts law also allows tenants to temporarily have a household member who is a minor child or elderly/disabled relative as a guest without violating guest policies. For longer stays, tenants generally have the right to sublet or assign their rental agreement with reasonable restrictions set by the landlord.
Victims of domestic violence, sexual assault, stalking, or other types of gender-based violence are also afforded protections. They have the right to request lock changes, terminal a rental agreement early, and cannot be evicted or refused tenancy due to their status as a victim.
Landlord Rights and Access
Landlords in Massachusetts have the right to access rental units for legitimate business purposes such as making necessary repairs, inspecting for damage, or showing the unit to prospective tenants or buyers. However, this right is not absolute, and landlords must follow specific rules and provide proper notice before entering.
Landlords must give tenants reasonable advance notice, typically 24 hours, before entering a rental unit except in cases of emergency. The notice should state the intended purpose and approximate time of entry. Landlords cannot abuse this right by making frequent entries without proper justification.
Permissible reasons for landlord entry include:
- Responding to repair requests from the tenant
- Making planned, periodic inspections for maintenance
- Showing the unit to prospective tenants (towards the end of a lease)
- Showing the unit to prospective buyers if the property is for sale
- Performing routine maintenance or services (e.g. pest control)
- Investigating potential lease violations
- Handling emergencies that threaten health or property
If a tenant unreasonably denies the landlord lawful access after proper notice, the landlord can pursue remedies through the court system. This may include terminating the tenancy for violation of the lease agreement. However, landlords cannot resort to extreme measures like changing the locks or removing the tenant's belongings without court approval.
Tenants have the right to peaceful enjoyment of their home. Landlords who abuse access privileges or enter without proper justification may be liable for harassment or privacy violations. Maintaining a professional landlord-tenant relationship with mutual respect for each party's rights is essential.
Eviction Laws
Eviction in Massachusetts is a legal process that landlords must follow precisely to remove a tenant from a rental property. The process is designed to ensure that tenants' rights are protected and that landlords have legitimate grounds for eviction.
Grounds for Eviction
Common grounds for eviction in Massachusetts include nonpayment of rent, violation of lease terms, creating a nuisance, or damaging the property. Landlords cannot evict tenants in retaliation for exercising their legal rights, such as requesting repairs or reporting housing code violations.
Notice Requirements
Before initiating an eviction, landlords must provide tenants with proper written notice:
- 14-Day Notice: For nonpayment of rent.
- 30-Day Notice: For terminating a month-to-month tenancy without cause.
- Other Notices: For lease violations, the notice period can vary depending on the severity and nature of the violation.
Eviction Process
If the tenant does not comply with the notice, the landlord must file an eviction lawsuit, known as a Summary Process, in the appropriate court. The tenant will receive a court summons and has the right to respond and attend a hearing.
Court Hearing
At the eviction hearing, both the landlord and tenant can present their case. If the judge rules in favor of the landlord, an execution order will be issued, allowing law enforcement to carry out the eviction if the tenant does not leave voluntarily.
Tenant Defenses
Tenants can raise several defenses during the eviction process, such as improper notice, retaliation, discrimination, or the landlord’s failure to maintain the property in a habitable condition.
Post-Eviction
After the court orders an eviction, tenants typically have a few days to move out before law enforcement enforces the order. Tenants may still have opportunities to resolve the issue, such as paying overdue rent in some cases.
Resources and Protections
Massachusetts law provides additional protections for tenants, including the right to redeem the tenancy by paying all overdue rent plus fees before the eviction hearing. Tenants facing eviction can seek assistance from legal aid organizations and tenant advocacy groups to understand their rights and options.
Understanding and adhering to these eviction laws helps ensure a fair and lawful process for both landlords and tenants in Massachusetts.
Squatters' Rights in Massachusetts
In Massachusetts, squatters can gain legal rights to a property through a process called adverse possession. Adverse possession allows a squatter to claim ownership of a property if they meet specific legal requirements over an extended period.
Requirements for Adverse Possession
To claim adverse possession in Massachusetts, a squatter must occupy the property openly, continuously, and without the owner's permission for a period of 20 years. The occupation must be:
- Open and Notorious: The squatter must occupy the property visibly, so the owner is on notice of the adverse possession.
- Exclusive: The squatter must possess the property exclusively, without sharing control with others, including the owner.
- Continuous: The occupation must be uninterrupted for the entire statutory period.
- Hostile: The possession must be without the owner’s permission and against the owner's interests.
Legal Process
If these conditions are met, the squatter can file a claim in court to obtain legal title to the property. The court will evaluate whether the requirements of adverse possession have been satisfied before granting ownership.
Property Owner Actions
Property owners should regularly inspect their properties and address any unauthorized occupancy promptly to prevent squatters from establishing a claim. Taking legal action early can prevent squatters from meeting the adverse possession requirements.
Understanding these laws can help both property owners and potential adverse possessors navigate their rights and responsibilities under Massachusetts law.
Resolving Landlord-Tenant Disputes
Open communication and a willingness to compromise are key when resolving disputes between landlords and tenants in Massachusetts. If issues arise, it's best for both parties to discuss the situation calmly and try to reach a mutually agreeable solution.
When disputes cannot be resolved through discussion, mediation services are available to help facilitate productive negotiations. Many community mediation programs provide affordable or free mediation assistance specifically for landlord-tenant matters.
If compromise cannot be reached, landlords and tenants can file claims in small claims court. The court process allows both sides to present evidence and make their case before a judge. Monetary damages, orders for repairs, and even eviction can result from small claims judgments.
Tenants dealing with difficult landlords or habitability issues can seek help from tenant advocacy groups and legal aid organizations. These nonprofits provide advice, education on rights, and potential representation for tenants struggling with unresponsive or uncooperative landlords.
No matter the dispute, open communication, willingness to compromise, and understanding of tenant rights are essential for resolving landlord-tenant conflicts properly under Massachusetts law.
Additional Resources
Massachusetts provides several resources to help tenants and landlords understand their rights and responsibilities under state law. The Massachusetts Department of Housing and Community Development offers information guides and resources covering topics like the eviction process, security deposits, and housing discrimination. Local housing authorities and city/town offices can also provide guidance on rental regulations specific to each municipality.
For low-income tenants, legal aid organizations like the Volunteer Lawyers Project, Massachusetts Law Reform Institute, and Harvard Legal Aid Bureau offer free or low-cost legal assistance with landlord-tenant disputes. These groups can help tenants understand their rights, negotiate with landlords, and represent them in housing court if needed.
Several nonprofit organizations also publish detailed handbooks explaining Massachusetts rental laws in plain language. The Massachusetts Union of Public Housing Tenants and Masslandlords.net provide comprehensive guides on topics like evictions, security deposits, and discrimination. These resources aim to educate both tenants and landlords.
Finally, statewide rental housing associations like the Greater Boston Real Estate Board and regional apartmentassociations.com offer member education, events, and advocacy around rental property ownership and management in Massachusetts. While aimed at landlords, their materials can shed light on industry practices and interpretations of state laws.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are my rights as a tenant at will in Massachusetts?
As a tenant at will in Massachusetts, you have the right to a habitable living environment, protection from discrimination, and reasonable notice before any changes to your tenancy, including rent increases or termination. Tenants at will must receive at least 30 days' notice before being required to move out, and they are entitled to due process in eviction proceedings.
What are the landlords' rights in Massachusetts?
Landlords in Massachusetts have the right to receive timely rent payments, enforce lease terms, and enter the rental unit for inspections or repairs with proper notice. They can also evict tenants for nonpayment of rent, lease violations, or creating a nuisance, provided they follow the legal eviction process. Landlords must maintain the property in a habitable condition and cannot retaliate against tenants for exercising their legal rights.
How much notice does a landlord have to give if not renewing a lease in Massachusetts?
In Massachusetts, if a landlord does not intend to renew a lease, they typically must provide the tenant with at least 30 days' notice before the lease term ends. This allows the tenant sufficient time to make alternative living arrangements. For fixed-term leases, no additional notice is required if the lease naturally expires at the end of its term, but it is good practice to communicate intentions clearly.
How much notice does a landlord have to give a tenant to move out in Massachusetts?
For terminating a month-to-month tenancy, a landlord must give the tenant at least 30 days' written notice. If the tenant is being evicted for nonpayment of rent or another lease violation, the landlord must provide a 14-day Notice to Quit. The notice period may vary based on the specific circumstances and grounds for eviction.
How long does it take to evict a tenant at will in Massachusetts?
The eviction process for a tenant at will in Massachusetts can take several weeks to a few months, depending on various factors. After providing the required 30-day notice, the landlord must file a Summary Process action in court if the tenant does not vacate. The court hearing and subsequent enforcement of the eviction order can add additional time to the process, especially if the tenant contests the eviction or requests a delay.
For more detailed information, you can refer to the Massachusetts Trial Court Law Libraries.