Vermont Tenant-Landlord Rental Laws & Rights for 2025
Vermont has a comprehensive set of laws governing the relationship between landlords and tenants. These laws aim to balance the rights and responsibilities of both parties, ensuring fair treatment and a safe, habitable living environment for renters. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, providing an in-depth overview of Vermont's tenant-landlord laws and regulations.
Whether you're a tenant seeking to understand your rights or a landlord looking to comply with legal obligations, this guide will equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the rental landscape in Vermont. From lease agreements and security deposits to housing quality standards and termination procedures, we'll cover all the essential aspects of the landlord-tenant relationship. Additionally, we'll explore tenant protections against discrimination, landlord access rights, and remedies for tenants when repairs are needed.
By familiarizing yourself with these laws, you'll be better prepared to address any issues that may arise during the rental process, ultimately fostering a more harmonious and legally compliant relationship between landlords and tenants in Vermont.
Residential Leases and Rental Agreements
In Vermont, both written leases and oral rental agreements are legally binding contracts between landlords and tenants. However, it's strongly recommended to have a comprehensive written agreement to avoid misunderstandings and disputes.
A lease is a contract for a fixed term, such as 6 months or 1 year, while a rental agreement typically renews automatically on a month-to-month basis unless proper notice is given by either party to terminate the tenancy.
Requirements for a Valid Lease or Rental Agreement
While not legally required, it's best practice for written agreements to include:
- Names of all tenants and landlords
- Description of the rental unit (address, number of rooms, etc.)
- Term of the rental period and provisions for renewal
- Rent amount and due date
- Responsibilities for utilities and maintenance
- Rules regarding pets, guests, smoking, etc.
- Procedures for termination or extension of the agreement
Key Provisions to Include
Rent Payment Requirements: Specify accepted payment methods, grace periods, late fees, etc.
Security Deposit Disclosures: Detail the amount required, permitted deductions, and return procedures.
Maintenance Responsibilities: Clearly outline duties of landlords vs. tenants.
Entry Provisions: Establish rules for landlord's entry into the unit.
Termination Clauses: Describe proper notice periods and conditions for terminating the agreement.
Both parties should carefully review all terms before signing a lease or rental agreement. Tenants have the right to negotiate provisions or get clarification on items they don't fully understand.
Security Deposits
There is no legal limit on the amount a landlord can charge for a security deposit in Vermont. However, the deposit must be reasonable in relation to the potential damages and rent amount. Many landlords charge the equivalent of one or two months' rent as a standard security deposit.
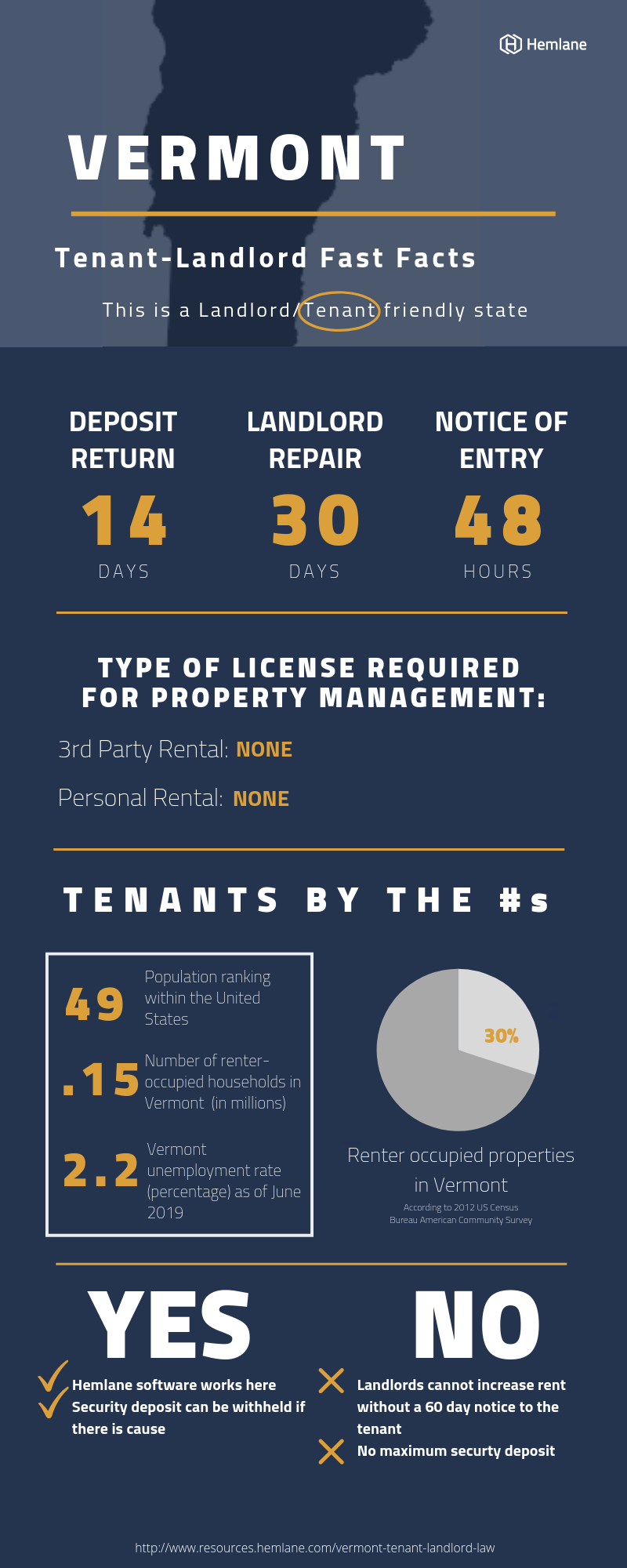
When it comes to returning security deposits, Vermont law requires landlords to provide a written statement detailing any deductions from the deposit within 14 days after the tenant moves out. Allowable deductions include unpaid rent, damages beyond normal wear and tear, and any other breaches of the lease agreement.
If the landlord fails to provide this statement and return any remaining deposit within the 14-day window, the tenant can seek a court order requiring the full deposit to be returned, plus a penalty of twice the amount wrongfully withheld and reasonable attorney's fees.
For tenants, it's essential to document the condition of the rental unit through photos or video before moving in and after moving out. This evidence can help dispute any unfair deductions from the deposit. Tenants should also request a walk-through inspection with the landlord when moving out to discuss any potential damages and deductions.
Another tip for tenants is to provide the landlord with a forwarding address in writing when moving out, as this starts the 14-day clock for the return of the deposit. Keeping meticulous records of rental payments and any communications with the landlord can also help protect tenant rights regarding security deposits.
Rent Increases and Rent Control
Landlords in Vermont must provide tenants with proper written notice before increasing the rent. The notice period required depends on the lease term:
- For tenancies of less than one year, 60 days' notice is required.
- For tenancies of one year or more, 90 days' notice must be given.
Vermont does not have statewide rent control laws, allowing landlords to set rental prices based on market conditions. However, some localities, like the city of Burlington, have implemented rent control regulations that limit how much landlords can increase rent each year. The maximum allowable rent increase in these areas is often tied to the Consumer Price Index (CPI). Landlords must provide tenants with a rent increase notice stating the new rent amount and the basis for the increase calculation.
For tenants living in subsidized housing, such as Section 8 properties, rent increases follow different rules set by the subsidized housing program. Typically, rent can only be increased once per year, and tenants must receive proper notice, often 30-60 days, before the increase takes effect. Rent adjustments in subsidized housing are based on factors like changes in family income or composition.
These regulations ensure that tenants in Vermont are given adequate notice of rent increases and that, in areas with rent control, increases remain reasonable and tied to economic indicators. This promotes fairness and stability in the rental market while allowing for necessary adjustments based on market conditions.
Housing Quality Standards
Vermont's Rental Housing Health Code establishes minimum standards for the safety, sanitation, and habitability of rental housing units statewide. This code covers essential aspects such as heating, utilities, smoke detectors, lead paint, appliances, and contaminants.
Heating requirements mandate that landlords provide a permanent heating system capable of maintaining a minimum temperature of 65°F in all habitable rooms during the cold months. Tenants are responsible for paying utility costs unless otherwise specified in the rental agreement.
Smoke detectors must be installed and maintained in operational condition in all rental units. Landlords are required to provide and replace batteries as needed. Carbon monoxide detectors are also mandatory in units with fossil fuel-burning appliances or attached garages.
Lead-based paint poses a significant health hazard, especially for children. Landlords must disclose the presence of lead-based paint hazards in pre-1978 housing units and follow specific renovation and maintenance protocols to minimize exposure risks.
All essential appliances, such as stoves, refrigerators, and heating systems, must be in good working condition and properly installed. Landlords are responsible for maintaining these appliances and promptly addressing any defects or malfunctions.
The code also addresses potential contaminants like mold, asbestos, and radon. Landlords must take appropriate measures to identify and mitigate any hazardous substances present in rental units, ensuring a safe living environment for tenants.
Compliance with the Rental Housing Health Code is crucial for maintaining habitable conditions and protecting the health and safety of tenants. Tenants have the right to report violations to local authorities, and landlords who fail to address code violations may face penalties and legal consequences.
Tenant Protections Against Discrimination
Vermont has strong laws in place to protect tenants from discrimination in housing. Both state and federal fair housing laws prohibit landlords from discriminating against tenants or prospective tenants based on certain protected characteristics.
At the federal level, the Fair Housing Act makes it illegal to discriminate in the rental, sale, or financing of housing on the basis of race, color, national origin, religion, sex, familial status, and disability. In Vermont, additional protected classes include age, marital status, sexual orientation, gender identity, and receipt of public assistance.
Landlords cannot refuse to rent, impose different rental terms, or otherwise make housing unavailable to someone because they belong to one of these protected classes. Discriminatory statements in advertising, refusing reasonable accommodations for disabilities, or enforcing overly restrictive occupancy standards could also violate fair housing laws.
Tenants with disabilities are entitled to reasonable accommodations that allow them equal opportunity to use and enjoy their rental unit. This could include allowing an assistance animal despite a "no pets" policy, or making reasonable physical modifications to the unit. However, the accommodation cannot impose an undue financial or administrative burden on the landlord.
Vermont's fair housing laws apply to nearly all housing, including private housing and most subsidized multi-family units. Tenants who experience discrimination should file a complaint with the state's Human Rights Commission or the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD).
Landlords’ Right of Access
Tenants in Vermont have a reasonable expectation of privacy in their rental units. While landlords maintain certain rights to access the property, there are limitations on when and how they can enter a tenant's home.
Landlords must provide at least 48 hours' advance notice before entering a rental unit, except in cases of emergency. This notice should be in writing and state the intended date, approximate time frame, and purpose for entry. Tenants have the right to be present during the landlord's entry unless it is truly impractical or unnecessary.
Permissible reasons for a landlord to enter include making repairs or inspections, showing the unit to prospective tenants or purchasers, or providing services outlined in the lease agreement. However, landlords cannot abuse this access to harass or intimidate tenants.
Except in emergencies like a fire or burst pipe, landlords cannot enter a rental unit without the tenant's consent if proper notice has not been provided. Tenants can pursue legal remedies if a landlord makes an illegal entry, such as recovering damages or terminating the rental agreement.
Tenants should never unnecessarily withhold consent for a landlord to enter when proper notice is given and the purpose is legitimate. However, they maintain the right to privacy and to refuse entry from a landlord who has not followed the appropriate procedures and requirements under Vermont law.
Tenant Remedies for Repairs
Under Vermont law, tenants have several remedies available if their landlord fails to make necessary repairs or maintain the rental unit in a habitable condition as required by the warranty of habitability. This implied warranty requires landlords to ensure the premises are safe, clean, and fit for human habitation.
One option for tenants is to withhold rent payments until the landlord addresses the issue. However, there is a specific procedure that must be followed. The tenant must provide written notice to the landlord detailing the problem and indicating their intention to withhold rent if it is not fixed within a reasonable time frame, typically 30 days. If repairs are still not made, the tenant can then legally withhold rent.
Tenants also have the "repair and deduct" remedy available. If the landlord fails to address a serious issue like lack of heat or running water after proper notice, the tenant can hire a licensed professional to make the repairs and deduct the cost from the rent payment. There are limits on how much can be deducted, and tenants must follow precise steps and keep detailed records.
It's important to note that tenants cannot withhold the full rent amount or use the "repair and deduct" option for minor issues. Serious violations that render the premises uninhabitable must exist. Tenants who improperly withhold rent or hire unlicensed contractors could be found in breach of the rental agreement. Consulting legal aid resources is advisable before exercising these remedies.
Evictions in Vermont
In Vermont, the eviction process is governed by state laws that outline specific requirements and procedures for terminating a tenancy. It is essential for both landlords and tenants to understand these laws to ensure that evictions are carried out legally and fairly.
No-Fault Evictions
For terminating a tenancy without cause (no-fault eviction), the notice period required depends on the type of rental agreement and the duration of the tenant's residency:
- Month-to-Month Tenancies: The landlord must provide at least 60 days' written notice. However, if the tenant has resided in the unit for less than two years, only 30 days' notice is required.
- Fixed-Term Leases: The landlord does not need to provide notice, as the tenancy ends automatically on the lease expiration date, unless otherwise stated in the lease.
Evictions for Cause
If the tenant has violated the rental agreement or lease terms, the landlord may pursue eviction for cause. The required notice period and the process depend on the nature of the violation:
- Standard Violations: For most lease violations, the landlord must provide a 14-day notice to quit, specifying the violation. The tenant then has 14 days to remedy the issue or vacate the premises.
- Serious Violations: If the violation involves substantial damage, injury, or code violations that pose a threat to health or safety, the landlord can terminate the tenancy with only a 7-day notice.
Illegal Evictions
Tenants in Vermont are protected against illegal evictions, such as self-help evictions (lockouts, utility shutoffs) or evictions without proper notice and court process. If a landlord attempts an illegal eviction, the tenant can seek injunctive relief from the court to regain possession and recover damages. It is crucial for both parties to follow the legal eviction process, which involves:
- Providing Proper Notice: The landlord must give the tenant a written notice specifying the reason for eviction and the required notice period.
- Filing a Complaint with the Court: If the tenant does not vacate after the notice period, the landlord must file an eviction lawsuit (known as an "action for possession") with the court.
- Obtaining a Court-Ordered Writ of Possession: If the court rules in favor of the landlord, it will issue a Writ of Possession, allowing law enforcement to remove the tenant from the property.
Following these steps ensures that the eviction process is conducted legally and that the rights of both landlords and tenants are respected. Understanding and adhering to Vermont's eviction laws helps prevent disputes and promotes a fair and orderly rental market.
Squatters' Rights in Vermont
In Vermont, squatters' rights are governed by the legal doctrine of adverse possession, which allows an individual to claim ownership of a property if they occupy it continuously and meet specific legal criteria over an extended period. Adverse possession laws are intended to ensure that property is used productively and to encourage property owners to monitor and maintain their land.
Criteria for Adverse Possession
To establish a claim of adverse possession in Vermont, a squatter must satisfy several criteria over a statutory period of 15 years. The key elements include:
- Actual Possession: The squatter must physically occupy the property, using it as an owner would. This includes living on the property, making improvements, or maintaining it.
- Open and Notorious: The possession must be visible and obvious to anyone, including the property owner. The squatter's presence should be apparent and not hidden, providing clear notice to the owner.
- Exclusive Possession: The squatter must be the sole occupant of the property, not sharing control with the owner or others.
- Hostile Possession: The occupation must be without the owner’s permission and against the owner’s interests. Hostility in this context means the squatter does not have legal authorization to be on the property.
- Continuous Possession: The squatter must occupy the property continuously for the entire statutory period without significant interruption.
Property Owners' Rights and Preventative Measures
Property owners in Vermont can take several steps to prevent adverse possession claims:
- Regular Inspections: Routinely inspecting and maintaining the property helps identify and address unauthorized occupancy promptly.
- Clear Boundaries: Erecting fences or posting signs can help establish clear property boundaries and deter squatters.
- Prompt Legal Action: Taking swift legal action to remove squatters can prevent them from meeting the continuous possession requirement.
- Granting Permission: Providing explicit permission for someone to use the property can negate the hostility requirement, thereby preventing an adverse possession claim.
Legal Process and Challenges
To establish a claim of adverse possession, a squatter typically needs to file a lawsuit to obtain a court judgment recognizing them as the legal owner of the property. The burden of proof lies with the squatter to demonstrate that all conditions of adverse possession have been met. Property owners can challenge these claims by presenting evidence that the criteria were not fulfilled, such as showing that the squatter’s possession was not continuous or that they had permission to be on the property.
Resources for Landlords and Tenants
Vermont offers a variety of resources to help both landlords and tenants understand their rights and responsibilities under state law. Educational materials are available through the Vermont Tenants Inc. organization, which provides guides, fact sheets, and seminars on topics like security deposits, rent increases, and the eviction process. The Vermont Landlords Association is a valuable resource for landlords, offering training, legal guidance, and best practices for property management.
For tenants facing issues with their housing situation, Vermont Legal Aid and the Vermont Human Rights Commission provide free legal assistance and can help file complaints related to discrimination, substandard living conditions, or other violations of tenant rights. The City of Burlington also has a dedicated Housing Resource Center that connects tenants with emergency rental assistance, housing counseling, and mediation services for resolving disputes with landlords.
Landlords in Burlington can access resources through the city's Code Enforcement Office, which provides information on rental housing regulations, property maintenance standards, and the rental inspection process. The office also offers educational workshops and one-on-one consultations to help landlords comply with local ordinances and ensure safe, habitable housing for their tenants.
Tenant-Landlord Balance in Vermont
Vermont's tenant-landlord laws aim to balance the rights and responsibilities of both renters and property owners. Key takeaways include the importance of well-drafted lease agreements, legal limits on security deposits, requirements for proper notice of rent increases and lease terminations, and the landlord's obligation to maintain habitable premises.
Tenants have robust protections against discrimination and unlawful entries by landlords. They also have remedies available if repairs are needed, such as using repair-and-deduct procedures or withholding rent in certain circumstances. At the same time, landlords can terminate leases upon proper notice for no stated reason or for violations like nonpayment of rent.
Both tenants and landlords would be wise to thoroughly understand their rights and obligations under Vermont law. The state's Rental Housing Health Code, fair housing statutes, security deposit rules, and termination notice periods are crucial considerations. Additional educational resources and organizations are available to help renters and property owners navigate tenant-landlord issues in Vermont.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the obligations of a landlord in Vermont?
Landlords in Vermont have several key obligations under state law. They must ensure rental units meet minimum housing quality standards, including providing adequate heat, water, and other essential services. Landlords must also respect tenants' privacy rights and follow proper procedures for entry. Perhaps most importantly, landlords must maintain rental properties in a safe and habitable condition under the implied warranty of habitability. Failure to address major repair issues can enable tenants to exercise rent withholding or "repair and deduct" remedies.
How much notice does a landlord have to give a tenant to move out in Vermont?
For month-to-month tenancies, landlords must provide 60 days' written notice to terminate the rental agreement without cause. For leases with defined terms, landlords can simply let the tenant know they don't intend to renew once the lease expires. However, if terminating a lease early for non-payment of rent or another violation, landlords must first issue a 14-day notice to quit. Termination notices must always meet the requirements under Vermont law.
How long before a guest becomes a tenant in Vermont?
Vermont law does not specify an exact timeline for when a guest becomes a tenant. However, if a person who is not on the lease stays for more than 30 consecutive days or moves in with the intent to remain permanently, they may establish tenant rights even without a written agreement. Landlords should be cautious about allowing long-term guests to avoid disputes over unauthorized tenants.
Is Vermont a landlord-friendly state?
Vermont's rental laws provide a balanced set of rights and responsibilities for both landlords and tenants. While the state has strong tenant protections like the warranty of habitability and anti-retaliation laws, landlords who follow the proper procedures can terminate non-compliant tenancies. Vermont does not have particularly stringent rent control or eviction laws compared to some other states. Overall, Vermont aims to ensure safe and habitable housing while respecting the contractual rights of landlords and tenants.
Get the Latest in Real Estate & Property Management!
I consent to receiving news, emails, and related marketing communications. I have read and agree with the privacy policy.





