Indiana Tenant-Landlord Rental Laws & Rights for 2025
Renting a home or apartment in Indiana comes with certain rights and responsibilities for both tenants and landlords. This guide provides an overview of the laws in Indiana that protect tenant rights and govern the landlord-tenant relationship.
The purpose of this guide is to help renters in Indiana understand their rights when it comes to issues like repairs, privacy, discrimination, security deposits, breaking a lease, and more. We'll cover the key questions and concerns renters in Indiana have about rental laws and provide clear answers based on the state's statutes and regulations.
Whether you're facing a dispute with your landlord, looking to break a lease, or just want to know what rules apply before signing a new rental agreement, this guide should provide the information you need to make informed decisions as a renter in Indiana. Having a strong grasp of your rights as a tenant will help ensure fair treatment, decent living conditions, and smooth interactions with your landlord.
Basic Rights of Tenants in Indiana
All tenants in Indiana have certain basic rights that are protected by state laws. These include:
Right to a Habitable Dwelling
Landlords in Indiana must provide premises that are fit for living according to building codes and standards for health and safety. This means the rental unit must have proper plumbing, heating, electricity, ventilation, and be structurally sound. The landlord is responsible for general maintenance and repairs to keep the property habitable.
Right to Privacy
Tenants have a right to privacy within their rental units in Indiana. The landlord must give proper advance notice before entering the unit, and can only enter for reasonable business purposes at reasonable times. Tenants are entitled to peaceful enjoyment of the rental property.
Right to Access Property
Landlords cannot lock out a tenant without obtaining a court order first. Tenants have a right to access, possess, and enjoy the rental property they are leasing. Illegal lockouts allow the tenant to recover damages or terminate the lease.
Protection from Discrimination
Landlords in Indiana cannot refuse to rent to or discriminate against potential tenants based on race, color, national origin, sex, religion, familial status, disability, ancestry, or military status. Tenants are protected against housing discrimination by federal and state fair housing laws.
Responsibilities of Landlords
Under Indiana law, landlords have a number of key responsibilities when it comes to renting out property. These include:
Provide Habitable Premises
Landlords are required to provide and maintain premises that are fit for occupation. This means ensuring rental units comply with applicable building and housing codes relating to health, safety, and maintenance. Landlords must provide proper plumbing, heating, ventilation, electricity, sanitation, and other facilities.
Make Repairs
Landlords in Indiana are responsible for making any repairs needed to keep the rental property habitable. This includes repairs to the structure itself as well as facilities like plumbing, heating, and electricity. Landlords cannot make tenants pay for repairs that would be considered normal wear and tear.
Maintain Common Areas
For properties with common areas like lobbies, stairwells, shared bathrooms, laundry rooms, and recreation areas, the landlord is required to keep these spaces clean and in good repair. They must maintain common areas in a sanitary and safe condition.
Give Proper Notice Before Entering
Landlords in Indiana need to give tenants reasonable advance notice before entering rental units, except in cases of emergency. Notice requirements depend on the purpose. For example, 48 hours written notice is required for repairs or maintenance, but no notice is needed in emergencies. This helps protect the tenant's right to privacy.
Handling Repairs and Maintenance Issues
When there is an issue with the rental unit that needs repair, Indiana law outlines the process tenants should follow to request maintenance and repairs from the landlord.
If something breaks, stops working properly, or becomes damaged in the rental unit, the tenant should notify the landlord in writing as soon as possible. The written request should describe the issue and requested repair in detail. The landlord must then begin making a good faith effort to fix the issue within 14 days for minor repairs, or 30 days for more serious issues impacting health or safety.
If the landlord fails to make the requested repairs in the required timeframe, the tenant has a few options:
- File a complaint with the local housing authority or building inspections department, who can inspect the unit and force repairs if violations are found.
- Hire a licensed contractor to make the repairs, and deduct the cost from future rent payments. Be sure to keep receipts and notify the landlord before taking this action.
- Sue the landlord in small claims court to recover damages related to the repair issue, including the cost of the repair, hotel costs if alternate housing is needed, etc.
- In severe cases, break the lease without penalty if the repair issue makes the unit uninhabitable or unfit to live in.
For minor, expected repairs like replacing HVAC filters or light bulbs, the tenant is usually responsible for the cost. For damage not caused by the tenant's actions, the landlord is generally responsible for the cost of repairs to maintain habitability and good working order. Tenants should never have to pay for repairs of pre-existing conditions.
Security Deposits
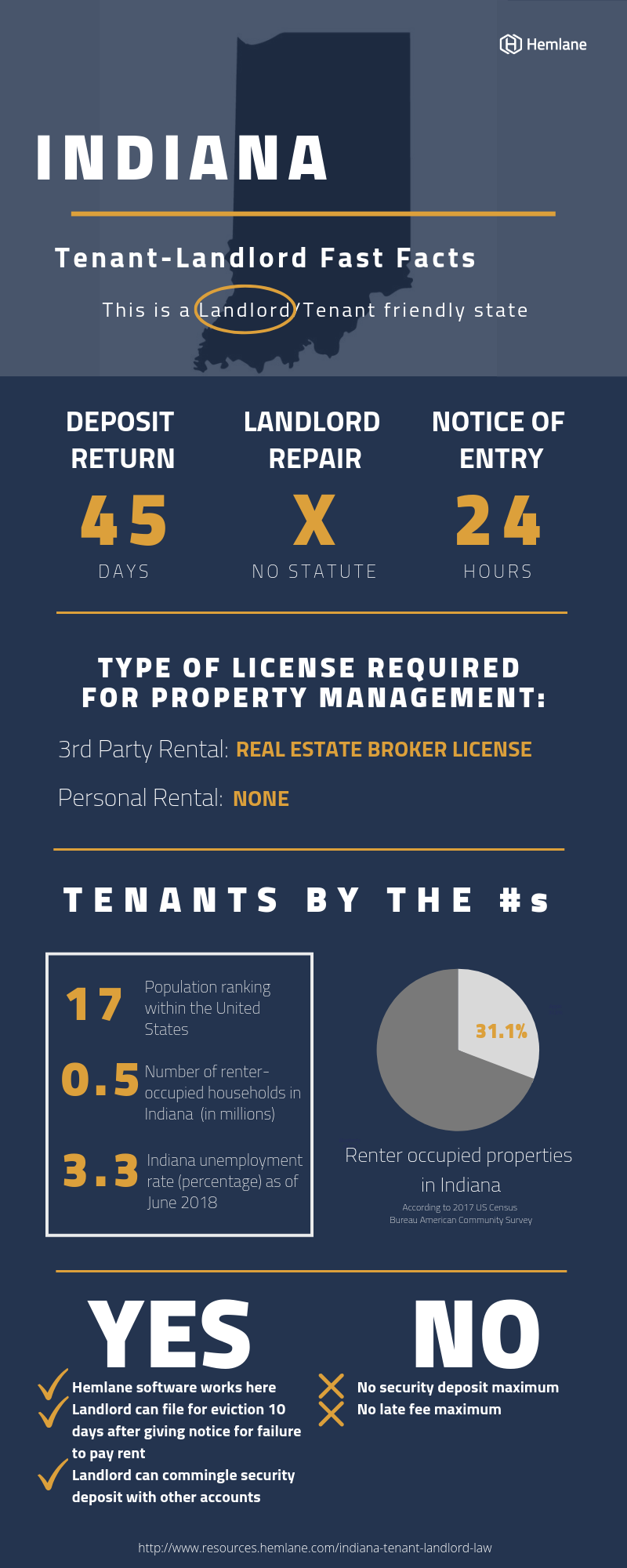
Security deposits are funds tenants pay to landlords at the beginning of a lease to cover any potential damages during the rental term. Indiana law regulates how much landlords can charge for security deposits as well as the process for returning deposits to tenants.
Limit on Security Deposit Amount
In Indiana, landlords cannot charge more than one month's rent for a security deposit, no matter the length of the lease. For example, if the monthly rent is $1,000, the maximum security deposit allowed is $1,000. Landlords also cannot require additional non-refundable fees at the beginning of a lease, with the exception of an application fee which is capped at $35 per applicant.
Returning the Deposit
When a tenant moves out at the end of a lease, the landlord has 45 days to return the security deposit together with an itemized list of any deductions. Reasons a landlord can deduct from the deposit include:
- Unpaid rent
- Damage to the property beyond normal wear and tear
- Costs of cleaning or repairing the unit for future tenants
- Late fees or other charges owed under the lease
If the landlord fails to return the deposit or provide a list of deductions within 45 days, the tenant can recover up to double the amount wrongfully withheld in small claims court.
Disputing Deductions
If a tenant disagrees with the deductions a landlord has taken from the security deposit, they should communicate in writing and attempt to resolve the dispute. If that fails, the tenant can file a lawsuit in small claims court against the landlord to recover the disputed amount. Having photographic evidence of the condition of the unit upon moving in and out is helpful in these cases.
Lease Agreements in Indiana
Lease agreements establish the rental terms between a tenant and landlord in Indiana. There are certain requirements that all leases must meet under state law.
Standard Lease Forms
While there is no standard lease form required in Indiana, most landlords use some type of written rental agreement. Verbal agreements are legal but more difficult to enforce. Written leases provide clearer terms and conditions for both parties.
Indiana law does not dictate specific provisions that must be included in rental agreements. But leases generally contain information like:
- Names of landlord and tenant
- Address of the rental unit
- Amount of monthly rent
- Due date for rent payments
- Late fees and returned check fees
- Security deposit amount and terms
- Lease start and end dates
- Tenant and landlord responsibilities
- Rules about guests, pets, smoking, etc.
Allowed and Prohibited Lease Terms
Landlords have broad discretion in setting lease terms. However, some specific provisions are restricted or banned under Indiana law:
No waiver of landlord duties
A lease cannot waive or limit a landlord's legal responsibilities, like providing a habitable residence.
No waiver of tenant rights
Tenants cannot sign away their rights under the law through a lease agreement.
No automatic lease renewal
Leases must have defined start and end dates. They cannot renew automatically without written consent.
No unreasonable fees
Leases cannot contain unreasonable late fees or other penalties meant to punish tenants.
Breaking a Lease in Indiana
Tenants who need to terminate a lease early should first check their rental agreement, as many leases allow this with proper notice and fees. If the lease does not allow early termination, the tenant can still try to negotiate an agreement with the landlord.
If the landlord does not agree, the tenant may be able to legally break the lease by proving:
- The unit is uninhabitable due to the landlord's failure to maintain it
- The landlord breached the lease terms
- Remaining in the unit would jeopardize the tenant's safety
Tenants who break a lease without legal justification can be sued by the landlord for any unpaid rent and costs of re-renting the unit. It's recommended to consult with a local tenant rights group before taking any action to terminate a lease early.
Rent Rules and Regulations
In Indiana, landlords must follow certain rules and regulations when it comes to rent payment and fees. Here's what tenants need to know:
Payment Due Dates and Grace Periods
- Rent is due each month on the date specified in the lease agreement, usually the 1st of the month.
- Tenants have a grace period before late fees can be charged. The grace period must be at least 5 days from the due date.
- If the 5th falls on a weekend or holiday, the grace period extends to the next business day.
- Rent is considered late if not paid by the end of the grace period.
Allowed Fees and Rent Increases
- Landlords cannot charge arbitrary fees not included in the lease. All fees must be agreed upon upfront.
- Indiana has no rent control laws. Landlords can raise rents to market rates with proper notice.
- For month-to-month leases, landlords must give 30 days written notice before raising rent.
- For annual leases, notice must be given 30 days before the end of the lease term.
Late Fees
- If rent is late, landlords can charge reasonable late fees, such as $50 or 5% of the monthly rent.
- Excessive late fees can be challenged in court. Fees over $10 or 5% may be deemed unfair penalties.
- Landlords cannot evict solely for nonpayment of late fees while rent is paid on time.
Eviction Process
Landlords in Indiana must follow proper procedures to legally evict a tenant. There are specific reasons a tenant can be evicted, as well as notice requirements and court procedures that must be followed.
Reasons a Tenant Can Be Evicted
A tenant in Indiana can be evicted for:
- Failure to pay rent
- Violating the rental agreement or rules
- Causing damage to the property
- Engaging in illegal activity
- Refusing the landlord access
- Staying after the lease terminates
The most common reason for eviction is nonpayment of rent.
Notice Requirements
Before a landlord can file for eviction, they must provide proper notice to the tenant. This includes:
- A 10-day notice to pay rent or vacate if the tenant has unpaid rent
- A 30-day notice for lease violations or holdover tenants
The notice must be in writing and describe the reason for eviction.
Eviction Court Procedures
If the tenant does not comply with the notice, the landlord can file an eviction lawsuit in small claims court. The tenant will be served notice of the court date.
At the hearing, both parties will present their case to the judge. If the judge rules in favor of the landlord, they will issue an eviction order.
The sheriff will then serve the eviction order giving the tenant 24 hours to vacate. If the tenant does not leave, the sheriff can forcibly remove them and their belongings.
Tenants who are evicted will have an eviction record, making it more difficult to rent in the future. It's recommended tenants try to remedy lease violations or work out agreements with landlords before reaching the eviction stage.
Getting Help and Legal Aid
If you are having issues with your landlord violating your rights as a tenant, there are resources available to help. Here are some options for getting assistance:
Housing Authorities and Tenant Resources
Most cities and counties have a local housing authority or tenant resource center. These organizations can provide information on your rights as a tenant, help mediate disputes, and assist with reporting violations. They may also offer legal services or help connect you with legal aid. Look up your local housing authority to see what services they offer tenants.
Seeking Private Legal Help
You may want to consult with a private attorney that specializes in landlord-tenant law. They can review your case, explain your options, and represent you if needed. Attorneys can help with issues like getting repairs made, recovering security deposits, fighting eviction, and suing for damages over violations. Look for a tenant lawyer or law firm in your area. Many offer free initial consultations.
Reporting Landlord Violations
If your landlord is violating your rights or breaking the law, you can file official complaints. This creates a record and paper trail. The state Attorney General's office takes complaints against landlords. Your local housing authority will also want to know about violations of housing codes and tenant laws. Reporting issues can lead to investigations and penalties against the landlord.
Getting advice and involving the right authorities can help resolve disputes with landlords. Don't be afraid to stand up for your tenant rights under Indiana law. These resources exist to help renters with landlord conflicts or violations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Tenants often have common concerns and questions when renting in Indiana. Here are answers to some of the most frequently asked questions:
What are some of the basic rights of tenants in Indiana?
- The right to a habitable dwelling that meets basic standards for health and safety
- Protection from illegal eviction and lockouts
- The right to privacy within the rental unit
- Protection from harassment or discrimination by the landlord
How much notice does my landlord need to give before entering my rental unit?
- 48 hours written notice is required for nonemergency purposes like showings or routine maintenance
- No notice is needed in cases of emergency
My landlord isn't making needed repairs. What can I do?
- Notify your landlord in writing and keep a dated copy
- Withhold rent until repairs are made, but keep the rent money available
- Seek legal action to recover damages or terminate the lease
When and how will I get my security deposit back?
- Within 45 days after you move out
- The landlord must provide an itemized list of any deductions
- You can recover double the deposit if it is wrongfully withheld
Can my landlord evict me without a court order?
No. Evictions require the landlord to go to court and get a judicial order. Self-help evictions like lockouts are illegal.
Who can I contact if I'm having issues with my landlord?
Contact the state attorney general's office, a local tenant advocacy group, or consult with a private attorney who handles landlord-tenant law.
The key takeaways are knowing your basic rights as a renter, following proper procedures for withholding rent or repairs, and seeking legal help when needed. Acting informed is the best way for tenants to avoid disputes and assert their rights.
Get the Latest in Real Estate & Property Management!
I consent to receiving news, emails, and related marketing communications. I have read and agree with the privacy policy.





